The Ultimate Guide to Choosing corrugated paper Slitting Blades for Flawless Production
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing Corrugated Paper Slitting Blades for Flawless Production
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Challenges in Corrugated Paper Slitting
- Decoding Blade Types: Plain Edge, Serrated, and Specialty Slitting Blades
- Material Matters: Selecting the Right Steel for Longevity
- Beyond the Basics: Blade Geometry and Performance Coatings
- Synergy with Machinery: The Role of the Corrugated Cardboard Packaging Machine
- Quick-Selection Guide: Matching Your Blade to the Job
Introduction
Achieving clean, consistent, and burr-free slits in corrugated paper is a critical determinant of packaging quality, machine uptime, and overall production cost. The wrong choice in slitting blades leads to frayed edges, excessive dust, accelerated wear, and costly unscheduled downtime. This definitive guide is engineered to solve these precise problems. We will demystify the selection process for industrial circular blades used in corrugated paper conversion, providing expert-backed insights on blade types, core materials, and application-specific configurations. By the end, you will possess the knowledge to specify blades that deliver flawless cuts, maximize lifespan, and protect your valuable corrugated cardboard packaging machinery.
1. Understanding the Challenges in Corrugated Paper Slitting
Corrugated board is a composite material, combining liners with a fluted medium. This structure presents unique cutting challenges distinct from solid paper or plastic film. The primary issue is the crushing of the flute during slitting, which weakens the board edge and creates dust. A blade must cleanly shear through the liners while cleanly parting the corrugated medium without compression. Furthermore, variations in board grade, adhesive content, and liner coatings demand a blade that can maintain its sharpness despite abrasive conditions. Selecting a generic circular blade not optimized for this task is a primary cause of poor edge quality and frequent blade changes.
2. Decoding Blade Types: Plain Edge, Serrated, and Specialty Slitting Blades
Not all slitting blades are created equal. The edge profile is your first and most crucial decision.
Plain Edge (Flat Knives): Ideal for achieving the smoothest, cleanest cut on high-quality, single-wall boards. They provide a shearing action but can generate more heat and pressure, potentially compressing softer flute structures if not perfectly sharp.
Serrated (Toothed) Edge Blades: The workhorse for most corrugated applications. The teeth grab and tear the liner and medium in a controlled manner, significantly reducing crushing force and dust generation. They are excellent for multi-wall, heavy-duty, or recycled boards. For specific non-woven or tricky materials, our serrated cutting blades offer tailored solutions.
Specialty Profiles (Score Slitters, Shear Cut): For kiss-cutting, perforation, or specific flute-direction slitting, custom ground profiles are necessary. These require consultation with an experienced manufacturer to match the blade geometry to the exact machine and product requirement.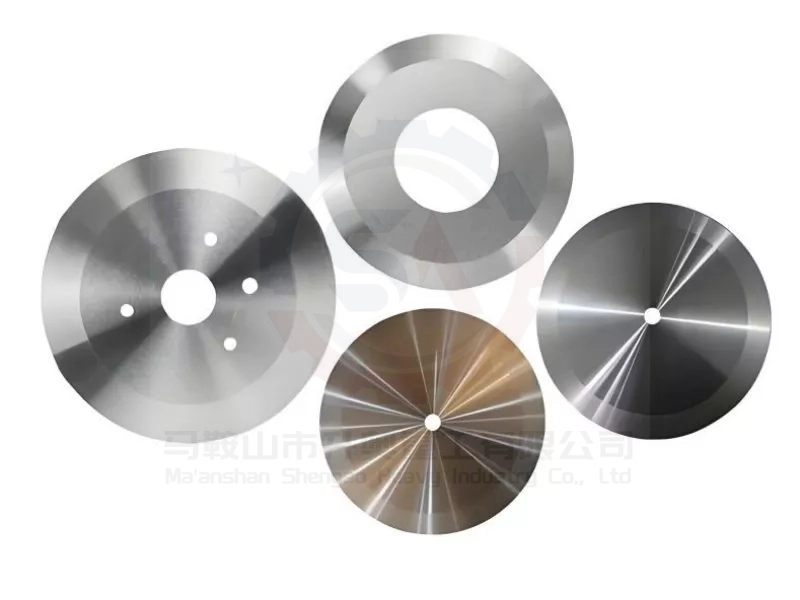
3. Material Matters: Selecting the Right Steel for Longevity
The base material of your blade dictates its wear resistance, toughness, and ability to hold a keen edge through miles of board.
High-Carbon Tool Steels (e.g., D2, A8): Offer an excellent balance of hardness and toughness for general corrugated slitting. They resist abrasion from silica in recycled liners and can be re-sharpened multiple times.
High-Speed Steel (HSS - M2, M35): Superior for high-volume, high-speed production lines. HSS retains its hardness at elevated temperatures generated by friction, preventing premature softening of the cutting edge. Our HSS cutting blades are engineered for these demanding environments.
Tungsten Carbide & Carbide-Tipped: The ultimate solution for extreme wear resistance. Tungsten carbide circular blades or carbide-tipped blades last exponentially longer than steel blades when cutting abrasive, glue-heavy, or coated liners. While the initial investment is higher, the total cost per linear meter of cut is often significantly lower.
4. Beyond the Basics: Blade Geometry and Performance Coatings
Precision grinding defines performance. The bevel angle, clearance angle, and surface finish of the blade are meticulously calculated to minimize cutting force and heat buildup. A perfectly balanced blade ensures vibration-free operation at high speeds, protecting your machine's spindles and bearings. Advanced surface coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Chromium Nitride (CrN) can be game-changers. These ultra-hard, low-friction coatings reduce adhesive build-up (a major issue with starch-based corrugating adhesives), further resist abrasion, and can extend service intervals by over 50%. Explore professional cutting blade solutions that incorporate these advanced geometries and treatments.
5. Synergy with Machinery: The Role of the Corrugated Cardboard Packaging Machine
The blade does not work in isolation; it is a critical component of the corrugated cardboard packaging machine ecosystem. This machinery, which includes flexo folder-gluers, rotary die-cutters, and slitter-scorers, demands absolute precision from its cutting tools. A mismatched or worn blade increases the load on drive motors, causes misalignment in downstream folding and gluing sections, and can lead to jams or defective boxes. The correct slitting blade ensures the machine runs at its optimal speed and accuracy, producing consistently dimensioned blanks that fold and seal perfectly. Regular blade inspection and maintenance are, therefore, integral to overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), preventing small blade issues from escalating into major machine downtime.
6. Quick-Selection Guide: Matching Your Blade to the Job
Use this table as a starting point for specifying your corrugated slitting blades. Always consult with your blade supplier for final recommendations based on your specific machine parameters.
| Board Type / Application | Recommended Blade Type | Recommended Material | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Wall, High-Quality Liner | Plain Edge or Fine Serration | D2 Tool Steel or HSS | Clean cut appearance is priority; manage speed to avoid heat. |
| Double/Triple-Wall, Recycled Board | Medium/Coarse Serrated Edge | HSS or Carbide-Tipped | Combating abrasion and preventing flute crush is critical. |
| High-Speed Production Line | Fine/Medium Serration | HSS with Coating (TiN) | Heat resistance and reduced friction for sustained performance. |
| Heavy Adhesive or Coated Liner | Serrated Edge with Anti-Stick Coating | Carbide-Tipped or Coated HSS | Preventing gumming and maintaining a free-cutting edge. |
| Kiss-Cutting/Perforation | Specialty Ground Profile | Tool Steel or HSS | Precise custom geometry required; consult manufacturer. |
Final Thoughts
Selecting the optimal slitting blade for your corrugated paper production is a technical investment that pays dividends in quality, efficiency, and total operating cost. It requires a holistic understanding of your material, machine dynamics, and production goals. By moving beyond a one-size-fits-all approach and leveraging the principles outlined in this guide—focusing on blade type, advanced materials, precision geometry, and system synergy—you transform a routine purchasing decision into a strategic performance upgrade. For engineers and production managers seeking to eliminate edge defects and maximize uptime, the path forward is clear: partner with a manufacturer that combines material science with practical application expertise. At ShengAo, we provide this precise blend of innovation and reliability, offering tailored corrugated paper cutting blade solutions designed to ensure flawless production from the first cut to the last.
